Introduction: Geography and Strategic Role of the Middle East
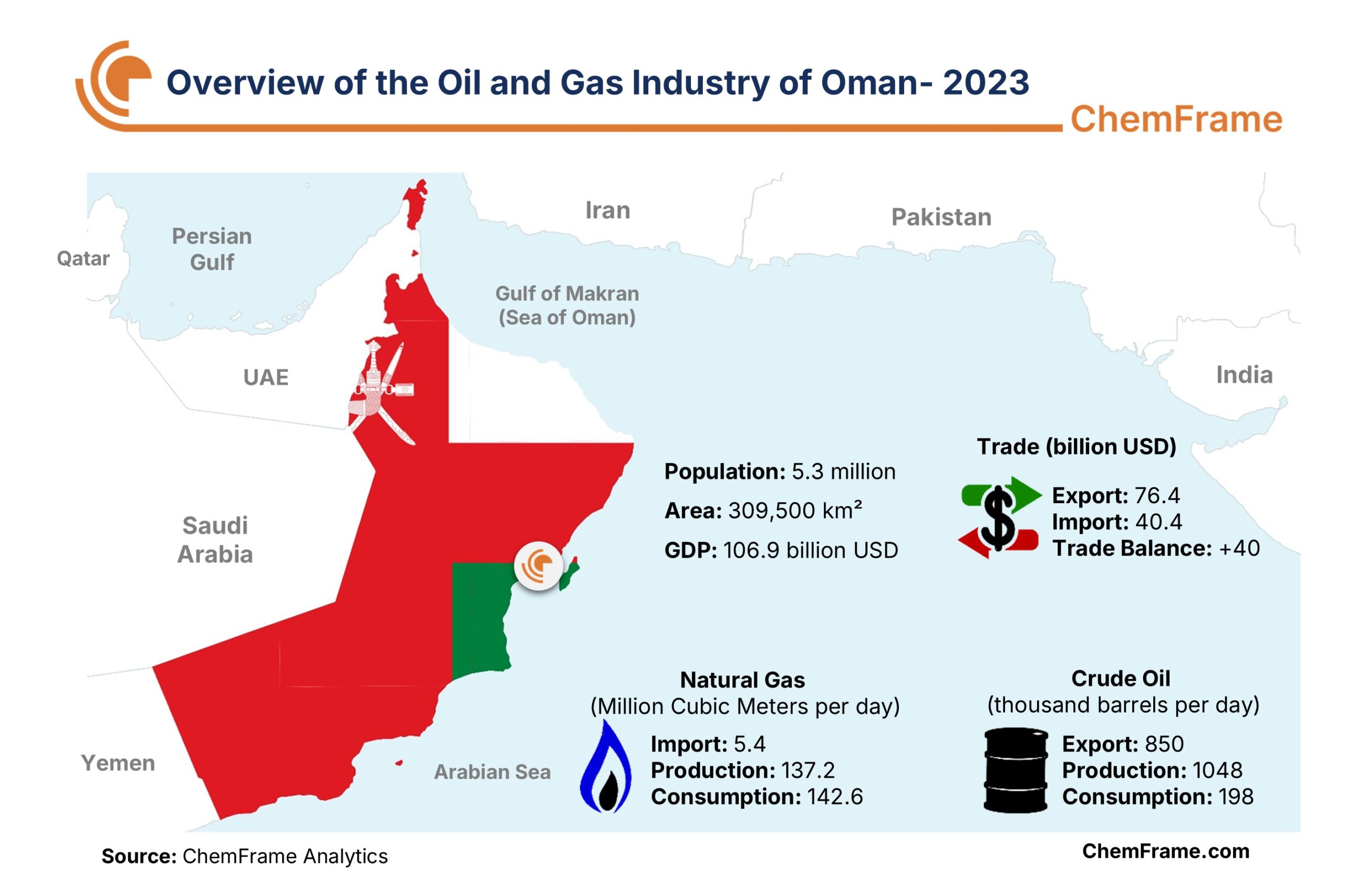
Oman, officially known as the Sultanate of Oman, is a monarchy located in the east of the Arabian Peninsula. The country is divided into 11 governorates, with Muscat as its capital, and its major cities include Sohar, Sur, Duqm, and Salalah. Oman has a population of approximately 4.6 million people and an area of around 309,500 square kilometers. The Middle East can be considered the most important player in the global oil and gas industry, as it holds half of the world’s proven crude oil reserves and one-third of its natural gas reserves. The value chain of many petroleum products and chemical derivatives has been developed in this region, granting it a significant role in the global economy.
Oman’s Oil and Gas Reserves and Production
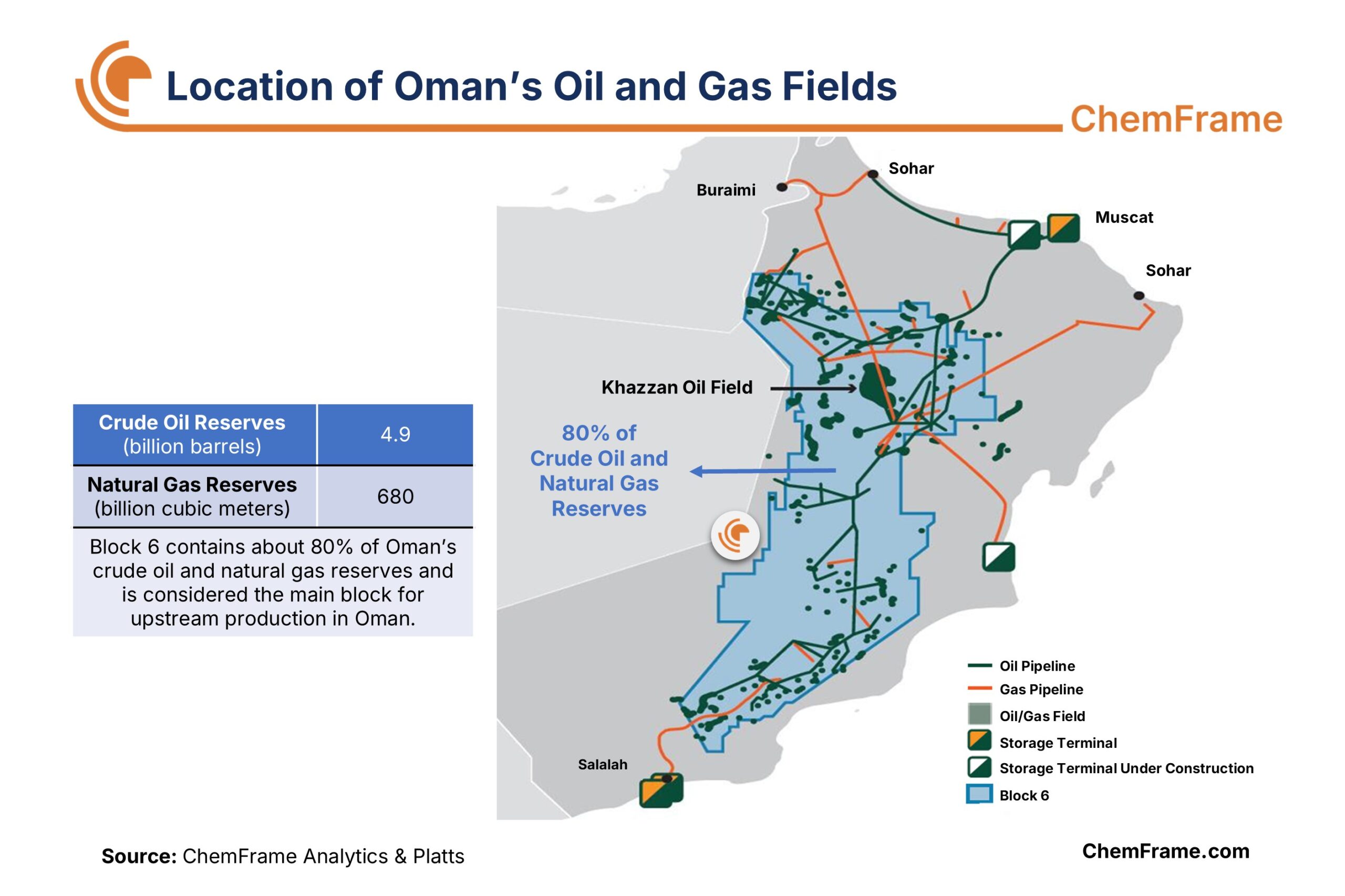
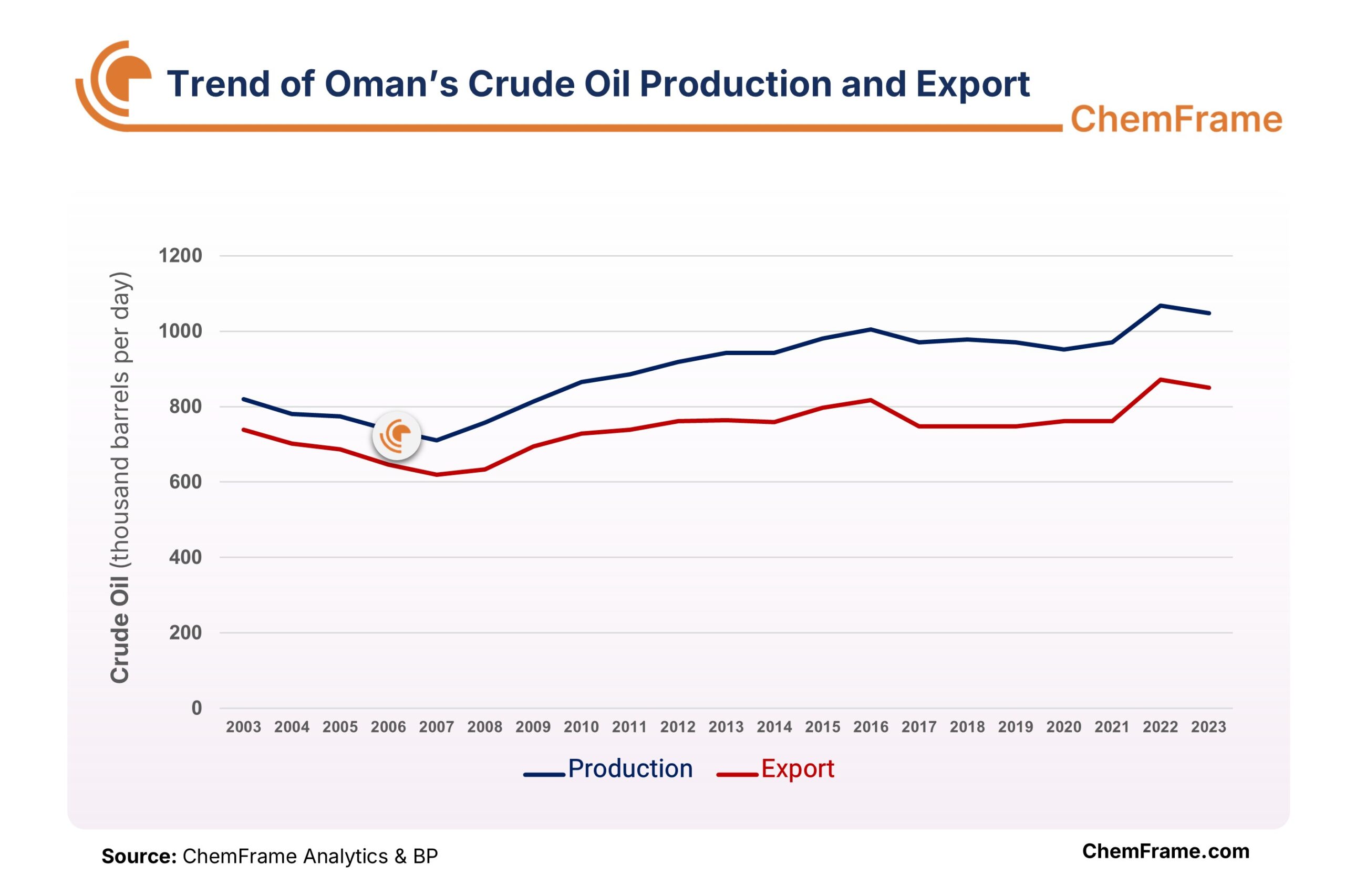
With 4.9 billion barrels of crude oil reserves and 680 billion cubic meters of natural gas reserves, Oman ranks 23rd and 28th globally in oil and gas reserves, respectively, and stands 7th in the Middle East. The country produces 1.048 million barrels of crude oil per day, of which 850 thousand barrels per day are exported. Oman also produces around 137.2 million cubic meters of natural gas per day and, along with importing 5.4 million cubic meters per day, meets its domestic demand of 142.6 million cubic meters per day. From 2010 to 2022, Oman’s natural gas production increased by approximately 50%, indicating the country’s economic growth and development and the rising demand for natural gas as a clean fuel. Although Oman’s oil and gas reserves are relatively small compared to other Middle Eastern and regional countries, its geopolitical position and low population have significantly contributed to the development of its oil and gas industry and Oman’s presence in the global energy market, creating attractive opportunities for investors.
Major Oil and Gas Fields
Most of Oman’s oil and gas fields are concentrated in Block 6, which contains about 80% of the country’s proven reserves. The main oil and gas fields include Barik, Fahud, Khazzan, Lekhwair, and Marmul.
Dependence on Oil Revenues and Export Markets
Oman is the largest non-OPEC oil producer, and its economy is significantly dependent on the oil and gas industry in Oman, with over 67% of government revenue derived from it. Omani crude is marketed under the name Oman Blend, with an API gravity of 32, classifying it as light crude oil. China is the primary destination for Oman’s crude oil exports, accounting for about 92% in 2023. Other key importers include India, Japan, and South Korea.
Refining Sector Development
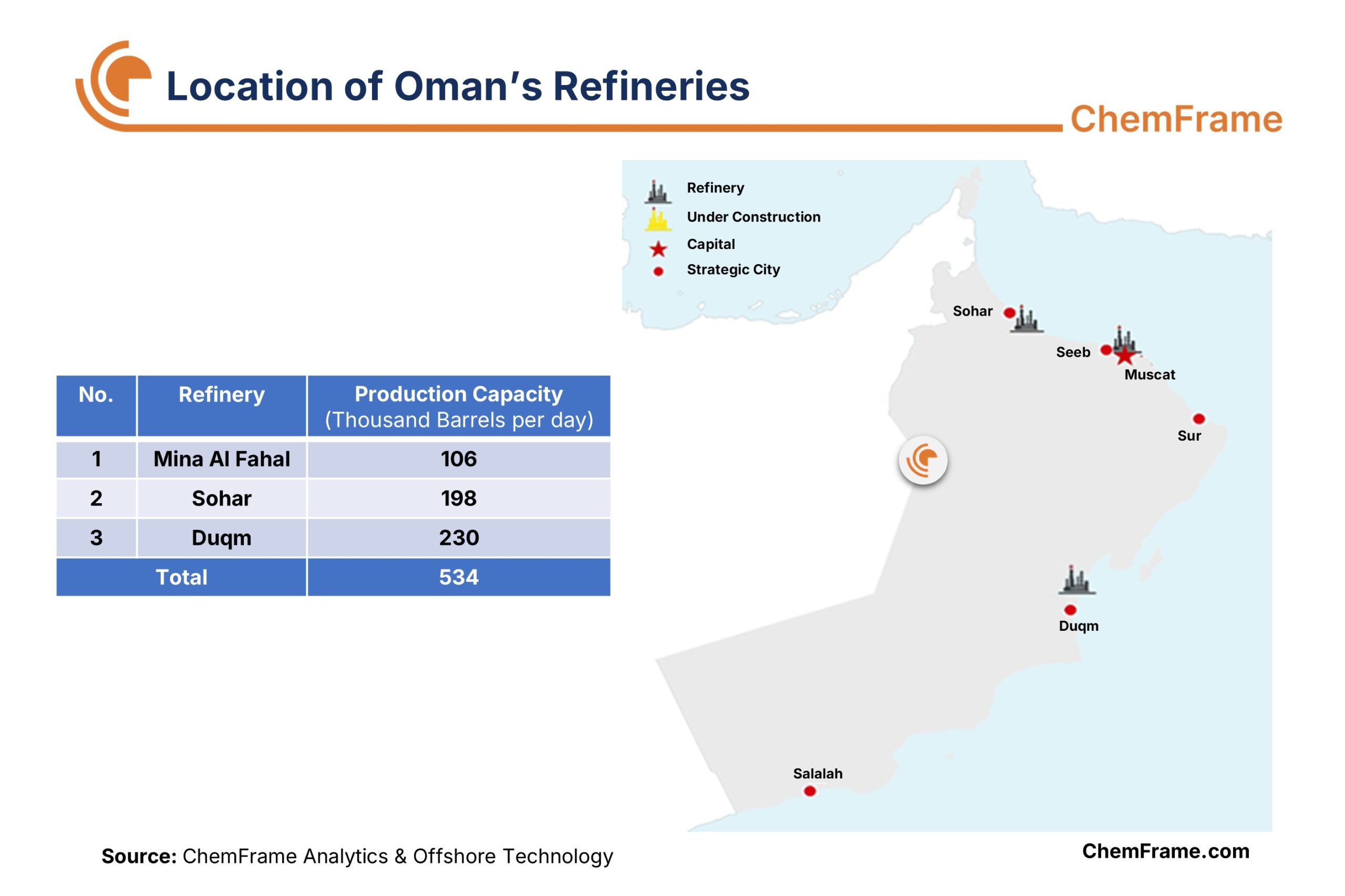
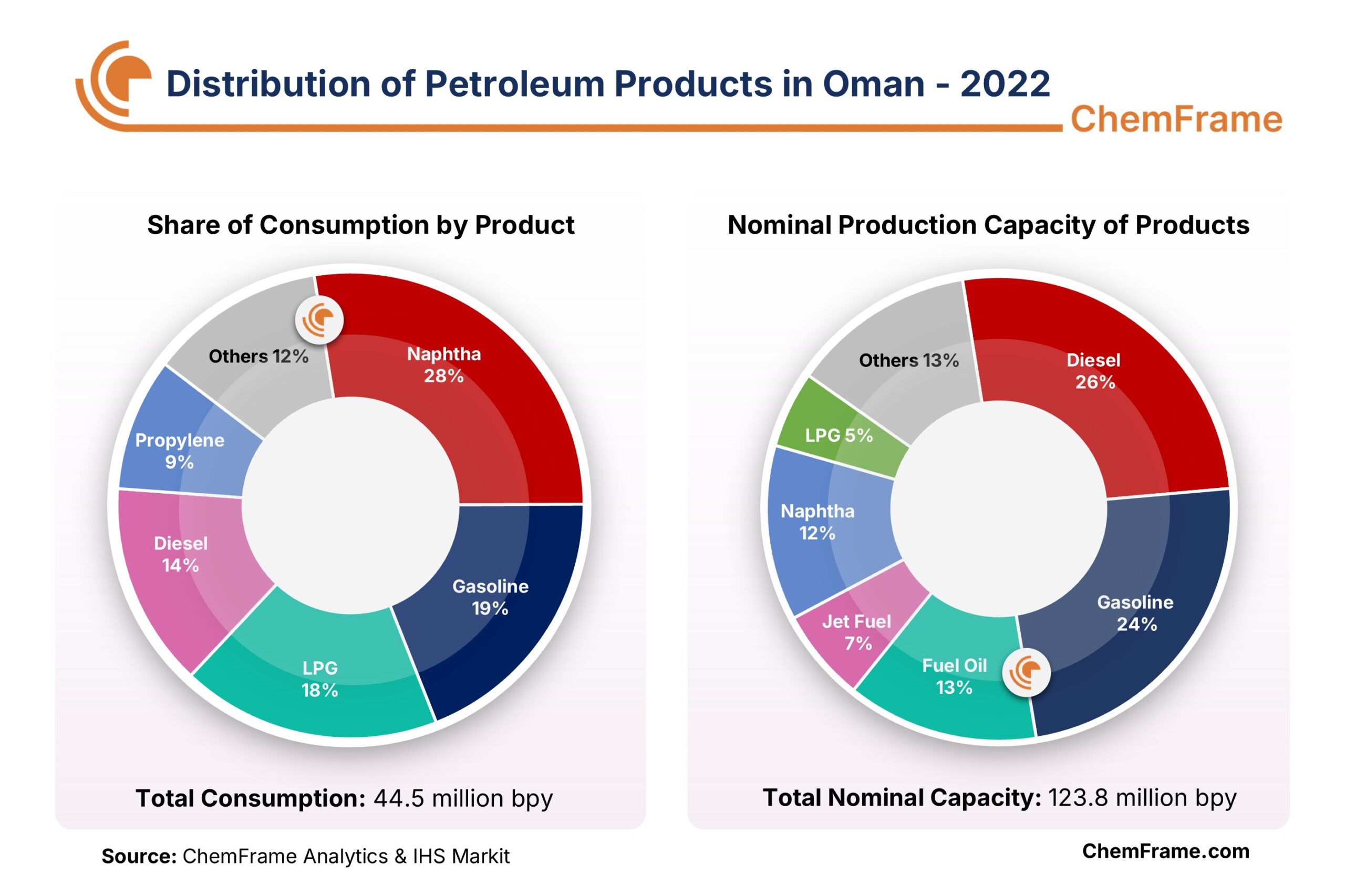
Oman has three refineries with a total combined capacity of 534 thousand barrels per day. Mina Al-Fahal, the first refinery in Oman, was established in 1982 with a processing capacity of 106 thousand barrels per day. The Sohar Refinery came into operation in 2006 with a capacity of 116 thousand barrels per day, but its refining capacity was later increased to 198 thousand barrels per day through recent modernization and expansion projects. The Duqm Refinery, with a processing capacity of 230 thousand barrels per day, was commissioned in late 2023 by the Oman-Kuwait joint venture, with each party holding a 50% share. Due to the strategic geographical location of the Duqm region—situated along one of the world’s most critical trade routes—the Duqm Refinery plays a vital role in supplying feedstock to Oman’s petrochemical industries.
Refined Products and Petrochemical Growth
Diesel and gasoline are considered the main refinery products of Oman. Naphtha is the most widely used refined product in the country, with around 81% of its production consumed domestically. It is also worth noting that all propylene produced in Oman is used locally for manufacturing products such as polypropylene.
In recent years, Oman has focused on increasing the utilization of its oil reservoirs and exploring new oil wells. At the same time, the country has sought to attract more foreign investment to apply new technologies, build refineries, and develop the midstream sector, while also expanding the export of refined products and boosting its petrochemical production.
Key Companies: PDO, Oman LNG, and OQ
The Petroleum Development Oman (PDO) is one of the leading companies in the exploration and production of oil and gas in Oman. It holds the largest share of Oman’s crude oil and natural gas production, and 60% of its shares belong to the government. PDO began its first oil exploration in 1962 and, in 1967, succeeded in exporting crude oil beyond Oman’s borders for the first time.
In 1994, Oman LNG L.L.C. was established by a royal decree to liquefy and market natural gas and condensate derivatives. Today, the company has the capacity to liquefy 11.4 million tons of natural gas per year.
In 2019, to drive Oman’s economic development and complete the oil and gas value chain, the OQ brand was introduced, integrating 9 major companies within Oman’s oil and gas industry. Among these companies are Orpic, Oman Oil Company, Oman Gas Company, Duqm Refinery, Salalah Methanol Company, and Salalah LPG.
OQ currently operates in 17 countries worldwide and covers the entire value chain—from oil and gas exploration and production, refinery and petrochemical operations, to marketing and distribution of end products in more than 80 countries. OQ produces a wide range of products, including amines, aldehydes, esters, alcohols, carboxylic acids, methanol, ammonia, and various grades of polyethylene and polypropylene.
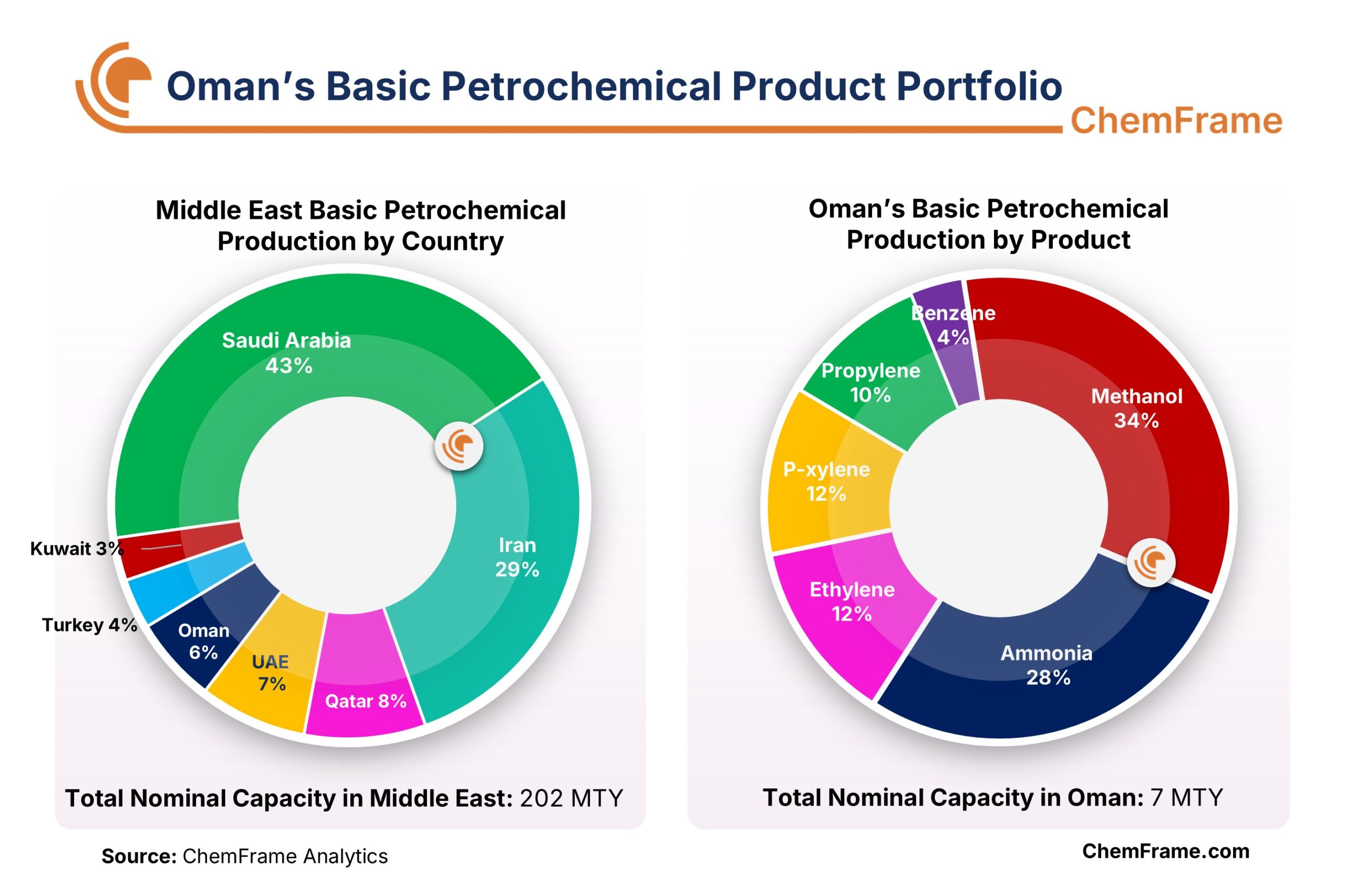
Oman’s production capacity of basic petrochemical products is approximately 7 million tons per year, with methanol and ammonia accounting for the largest share. Oman also produces 12 million tons out of the Middle East’s 202 million tons of major petrochemical products, making it the 5th-largest producer in the region.
Conclusion
At ChemFrame, we believe that since oil plays a crucial role in the economic development of resource-rich nations, analyzing the experiences and strategies of other oil-based economies—such as Oman and Saudi Arabia—is essential for shaping smarter development policies.
As noted earlier, more than 67% of Oman’s national revenue is derived from oil and gas. Despite this dependence, Oman has in recent years actively pursued foreign investment, new oil exploration, and increased production and exports. Recent large-scale projects and newly-established facilities—such as the Duqm Refinery and the Salalah Ammonia & Petrochemicals Complex—reflect the country’s clear strategy to further expand its midstream and downstream oil & gas sectors.
In recent years, Oman has transitioned from being solely a natural gas exporter to becoming a net importer of natural gas. In 2023, the country’s total natural gas supply (production plus imports) increased by around 3.6% compared to 2022. This ensured sufficient feedstock for downstream industries, while also enabling greater use of natural gas as a clean and cost-efficient energy source. Today, approximately 92% of Oman’s electricity is generated from natural gas, which has reduced the use of diesel in power generation by 26%.
Additionally, with the involvement of companies such as Oxy Oman and bp Oman, the country is intensifying its efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote the use of methanol and ammonia as green fuels.
Overall, Oman represents a strong example of a developing nation with a planned and balanced approach to growth—one that aims to achieve economic progress while also preserving its cultural identity and traditions. In recent years, the country has demonstrated notable economic advancement, including significant GDP growth, and has successfully achieved 89% workforce nationalization in its oil and gas sector.
FAQs
- Why is Oman considered an important player in the oil and gas industry?
Oman’s strategic location, stable regulatory environment, and expanding midstream and downstream investments make it a key player in the regional energy sector despite its moderate reserves. - How much of Oman’s government revenue comes from oil and gas?
Over 67% of Oman’s government revenue is derived from the oil and gas sector. - Which countries import the most crude oil from Oman?
China is the largest importer of Omani crude, accounting for around 92% of its oil exports, followed by India, Japan, and South Korea. - What are Oman’s main oil and gas reserves?
Most of Oman’s reserves are located in Block 6, which holds about 80% of the country’s proven oil and gas resources. - How many oil refineries does Oman have, and what are their capacities?
Oman operates three refineries—Mina Al-Fahal, Sohar, and Duqm—with a total refining capacity of 534,000 barrels per day. - What are the main refined petroleum products in Oman?
Diesel, gasoline, and naphtha are among the main refined products, with naphtha being the most consumed locally. - What is OQ, and what role does it play in Oman’s petrochemical industry?
OQ is a national integrated energy company that manages Oman’s full value chain—from exploration and refining to petrochemical production and global marketing. - What petrochemical products does Oman produce?
Oman produces methanol, ammonia, polyethylene, polypropylene, and various chemical intermediates such as amines, esters, and aldehydes. - How is Oman transitioning toward cleaner energy?
Oman is increasing gas-based power generation, reducing diesel use in electricity production, and investing in green fuels such as methanol and ammonia. - Is Oman investing in future downstream and midstream development?
Yes. Major projects such as the Duqm Refinery and Salalah petrochemical expansions show a strategic focus on developing midstream and downstream industries to diversify the economy.
